Toyota Venza: System Description
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1. NAVIGATION SYSTEM OUTLINE
(a) Vehicle position tracking methods
It is essential that the navigation system correctly tracks the current vehicle position and displays it on the map. There are 2 methods to track the current vehicle position: autonomous (dead reckoning) and GPS* (satellite) navigation. Both navigation methods are used in conjunction with each other.
*: GPS (Global Positioning System)
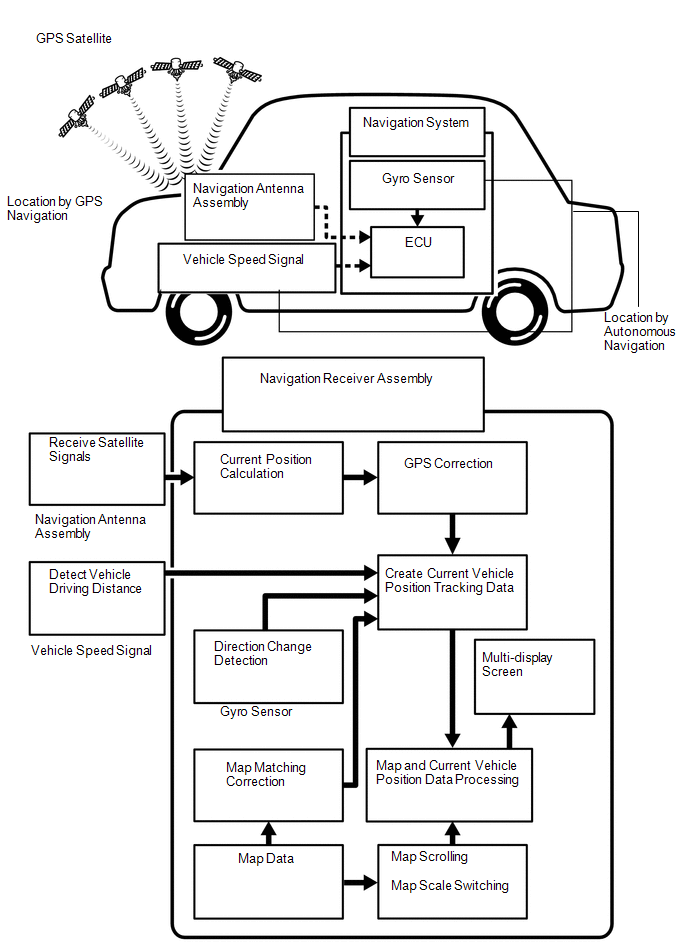
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Vehicle Position Calculation |
The navigation receiver assembly calculates the current vehicle position (direction and current position) using the direction deviation signal from the gyro sensor and driving distance signal calculated from the vehicle speed signal and creates the driving route. |
|
Map Display Processing |
The navigation receiver assembly processes the vehicle position data, vehicle driving track and map data from the SD card (disc player disc). |
|
Map Matching |
The map data from the SD card (disc player disc) is compared to the vehicle position and driving track data. Then, the vehicle position is matched with the nearest road. |
|
GPS Correction |
The vehicle position is matched to the position measured by the GPS. Then, the GPS measurement position data is compared with the vehicle position and driving track data. If the position is very different, the GPS measurement position is used. |
|
Distance Correction |
The vehicle speed signal includes errors caused by tire wear and slippage between the tires and road surface. Distance correction is performed to account for this. The navigation receiver assembly automatically offsets the signal to make up for the difference between it and the distance data of the map. The offset is automatically updated. |
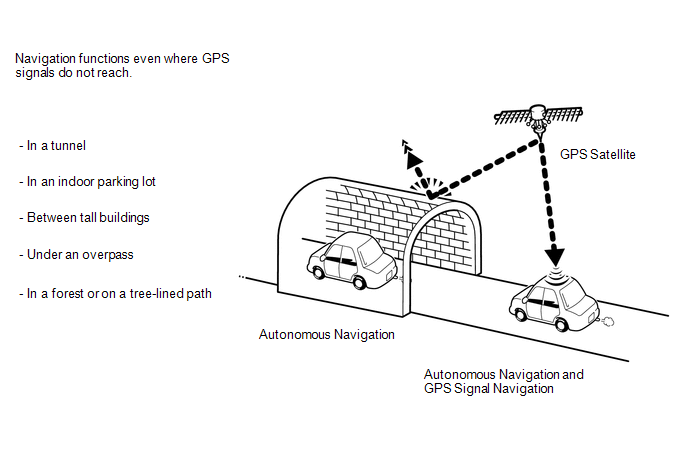
HINT:
The combination of autonomous and GPS navigation makes it possible to display the vehicle position even when the vehicle is in places where GPS signals cannot be received. When only autonomous navigation is used, however, the mapping accuracy may slightly decrease.
(b) Autonomous navigation
This method determines the relative vehicle position based on the driving track determined by the gyro sensor located in the navigation receiver assembly and the vehicle speed signal.
(1) Gyro sensor
Used to calculate the direction by detecting angular velocity. It is located in the navigation receiver assembly.
(2) Vehicle speed signal
Used to calculate the vehicle driving distance.
(c) GPS* navigation (Satellite navigation)
This method detects the absolute vehicle position using radio waves from GPS satellites.
*: GPS satellites were launched by the U.S. Department of Defense for military purposes.
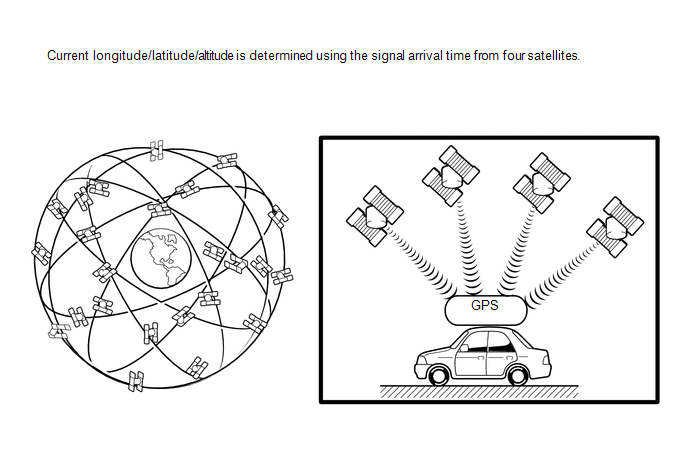
|
Number of Satellites |
Measurement |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
2 or less |
Measurement is impossible |
Vehicle position cannot be obtained because the number of satellites is not enough. |
|
3 |
2-dimensional measurement is possible |
Vehicle position is obtained based on the current longitude and latitude. (This is less precise than 3-dimensional measurement.) |
|
4 |
3-dimensional measurement is possible |
Vehicle position is obtained based on the current longitude, latitude and altitude. |
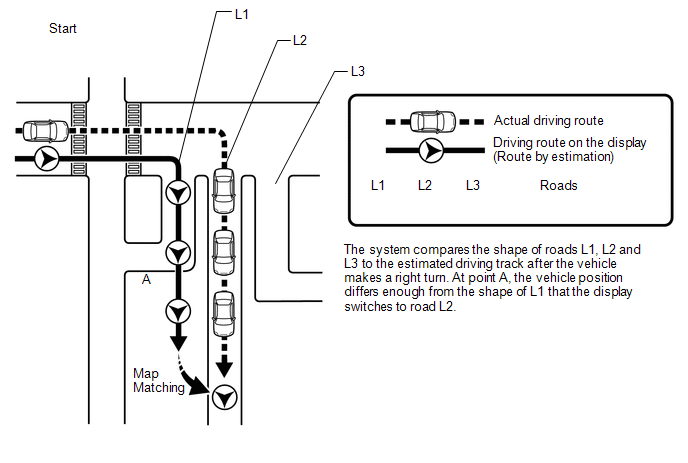
(d) Map matching
The current driving route is calculated by autonomous navigation (according to the gyro sensor and vehicle speed signal) and GPS navigation. This information is then compared with possible road shapes from the map data in the SD card (disc player disc) and the vehicle position is set onto the most appropriate road.
2. TOUCH SWITCH OUTLINE
(a) Touch switches are touch-sensitive (interactive) switches operated by touching the screen. When a switch is pressed, the outer film bends in to contact the inner glass at the pressed position. By doing this, the voltage ratio is measured and the pressed position is detected.
.png)
3. DISC PLAYER OUTLINE
(a) A disc player uses a laser pickup to read digital signals recorded on a disc. By converting the digital signals to analog, it can play music and audio.
CAUTION:
Do not look directly at the laser pickup because the disc player uses an invisible laser beam. Be sure to operate the player only as instructed.
NOTICE:
- Do not disassemble any part of the disc player.
- Do not apply oil to the disc player.
- Do not insert anything but a disc into the disc player.
(b) This player can play only audio CDs, CD-Rs (CD-Recordable) and CD-RWs (CD-ReWritable) that have any of the following marks:
.png)
(c) The following products may not be playable on your player.
- SACD
- dts CD
- Copy-protected CD
(d) Precautions for use of discs
NOTICE:
- CD-Rs and CD-RWs may not be played depending on the recording conditions or characteristics of the discs, or due to damage, dirt or deterioration caused by leaving the discs in the cabin for a long time.
- Unfinalized CD-Rs and CD-RWs cannot be played.
- CD-Rs and CD-RWs are more easily affected by a hot and humid environment than discs used for normal audio CDs. For this reason, some CD-Rs and CD-RWs may not be played.
- If there are fingerprints or scratches on a disc, the disc may not be played or the disc may skip.
- Some CD-Rs and CD-RWs may deteriorate if they are left in the cabin for a long time.
- Keep CD-Rs and CD-RWs in an opaque case.
- DualDiscs that mate DVD recorded material on one side with CD digital audio material on the other cannot be played.
- Keep discs away from dirt. Be careful not to damage discs or leave fingerprints on them.
- Hold discs by the outer edge and center hole with the label side up.
- Leaving a disc exposed halfway out of the slot for a long time after pressing the disc eject button may cause deformation of the disc, making the disc unusable.
- If discs have adhesive tape, stickers, disc labels or any traces of such labels attached, the discs may not be ejected or player malfunctions may result.
- Keep discs away from direct sunlight. (Exposure to direct sunlight may cause deformation of a disc, making the disc unusable.)
- Do not use odd-shaped discs because these may cause player malfunctions.
- Do not use discs whose recording portion is transparent or translucent because they may not be inserted, ejected or played normally.
- Use only 4.7 in. (12 cm) discs.
- Do not use 3 in. (8 cm) discs either with or without adaptors.
HINT:
- When it is cold or raining, if the windows fog up, mist and condensation may form in the player. In such cases, a disc may skip or stop in the middle of play. Ventilate or dehumidify the cabin for a while before using the player.
- A disc may skip if the player experiences strong vibrations when the vehicle is driven on rough roads or similar uneven surfaces.
(e) Cleaning
.png)
NOTICE:
Do not use a lens cleaner because it may cause a malfunction in the pickup portion of the player.
(1) If dirt is on the disc surface, wipe it clean with a soft dry cloth such as an eyeglass cleaner for plastic lenses from the inside to the outside in a radial direction.
NOTICE:
- Pressing on the disc by hand or rubbing the disc with a hard cloth may scratch the disc surface.
- Use of solvents such as record spray, antistatic agents, alcohol, benzine, thinners or a chemical cloth may cause damage to the disc, making the disc unusable.
4. USB AUDIO SYSTEM FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The No. 1 stereo jack adapter assembly is equipped with a USB terminal. Connecting a USB device or "iPod" to the No. 1 stereo jack adapter assembly allows music files to be played. Not only is it possible to play music from a USB device with audio functions, it is also possible to play MP3, WMA or AAC music files that are stored on a USB device. In addition, "iPod" control software is installed, allowing file selection from playlists and operation using shuffle mode.
HINT:
Operation through the controls of a USB device or "iPod" cannot be performed while it is connected.
(b) USB audio system compatible devices
(1) USB device
The following device formats can be used:
|
Compatible USB device formats |
|
MP3, WMA and AAC files written to a USB device with any format other than those listed above may not be played correctly, and their names and folder names may not be displayed correctly.
Items related to standards and limitations are as follows:
- Maximum directory hierarchy: 8 levels
- Maximum number of folders in device: 3000 (including the root folder)
- Maximum number of files in device: 9999
- Maximum number of files per folder: 255
(2) "iPod"
"iPhone", "iPod", "iPod classic", "iPod nano" and "iPod touch" are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
The following "iPod", "iPod nano", "iPod classic", "iPod touch" and "iPhone" devices can be used with this system.
Made for:
- "iPod touch" (5th generation)
- "iPod touch" (4th generation)
- "iPod touch" (3rd generation)
- "iPod touch" (2nd generation)
- "iPod touch" (1st generation)
- "iPod classic"
- "iPod with video"
- "iPod nano" (7th generation)
- "iPod nano" (6th generation)
- "iPod nano" (5th generation)
- "iPod nano" (4th generation)
"iPod nano" (3rd generation)
- "iPod nano" (2nd generation)
- "iPod nano" (1st generation)
- "iPhone 5"
- "iPhone 4S"
- "iPhone 4"
- "iPhone 3GS"
- "iPhone 3G"
- "iPhone"
HINT:
Depending on differences between models or software versions etc., some models might be incompatible with this system.
5. MP3/WMA/AAC OUTLINE
(a) Playable MP3 file standards
|
Compatible standard |
MPEG1 LAYER3, MPEG2 LSF LAYER3 |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
|
|
Compatible bit rate |
|
|
Compatible channel mode |
Stereo, joint stereo, dual channel, monaural |
(b) Playable WMA file standards
|
Compatible standard |
WMA Ver. 7, 8, and 9 |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
32, 44.1, 48 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate (Only compatible with 2-channel playback) |
|
(c) Playable AAC file standards
|
Compatible standard |
MPEG4/AAC-LC |
|
Compatible sampling frequency |
11.025, 12, 16, 22.05, 24, 32, 44.1, 48 (kHz) |
|
Compatible bit rate |
|
(d) ID3 tag, WMA tag and AAC tag
(1) Additional text information called an ID3 tag can be input to MP3 files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
HINT:
This player is compatible with ID3 tags of ID3 Ver. 1.0 and 1.1, and ID3 Ver. 2.2 and 2.3. (Number of characters complies with ID3 Ver. 1.0 and 1.1.)
(2) Additional text information called a WMA tag can be input to WMA files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(3) Additional text information called an AAC tag can be input to AAC files. Information such as song titles and artist names can be stored.
(e) Usable media
(1) Only CD-ROMs, CD-Rs (CD-Recordable), CD-RWs (CD-ReWritable) and USB devices can be used to play MP3/WMA/AAC files.
NOTICE:
- CD-Rs and CD-RWs are more easily affected by a hot and humid environment than discs used for normal audio CDs. For this reason, some discs may not be played.
- If there are fingerprints or scratches on a disc, the disc may not be played or may skip.
- Some CD-Rs and CD-RWs may deteriorate if they are left in the cabin for a long time.
- Keep CD-Rs and CD-RWs in an opaque case.
(f) Usable media format
(1) Usable media format
|
Disc format |
CD-ROM Mode 1 and Mode 2 CD-ROM XA Mode 2, Form 1 and Form 2 |
|
File format |
ISO9660 Level 1 and Level 2 (Romeo, Joliet) UDF (2.01 or lower) |
HINT:
- MP3/WMA/AAC files written in any unlisted format may not be played normally or the file names or folder names may not be displayed correctly.
- This player is compatible with multi-session discs and can play CD-Rs and CD-RWs on which MP3/WMA/AAC files have been added. However, only the first session can be played.
- Discs whose first session includes both music data and MP3, WMA and AAC format data may not be played.
(2) Standards and restrictions
|
Maximum directory levels |
8 levels |
|
Maximum number of characters for a folder name/file name |
32 characters |
|
Maximum number of folders |
192 (Including empty folders, root folders, and folders that do not contain MP3/WMA/AAC files) |
|
Maximum number of files in a disc |
255 (Including non- MP3/WMA/AAC files) |
(g) File names
(1) Only files with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma" and ".m4a" can be recognized and played as MP3, WMA or AAC files.
(2) Save MP3, WMA or AAC files with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma" or ".m4a".
NOTICE:
If non-MP3, non-WMA or non-AAC files are saved with an extension of ".mp3", ".wma" or ".m4a", those files may be wrongly recognized as MP3, WMA or AAC files and played. A loud noise may occur and damage to the speakers may result.
6. "Bluetooth" OUTLINE
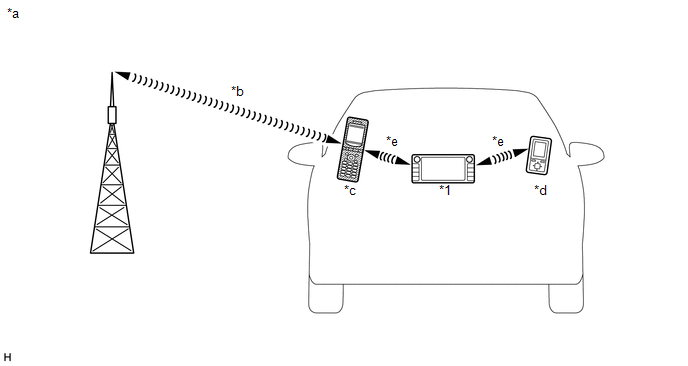 Text in Illustration
Text in Illustration
|
*1 |
Navigation Receiver Assembly (Built-in "Bluetooth" Antenna) |
- |
- |
|
*a |
Example |
*b |
Cellular Network |
|
*c |
Cellular Phone ("Bluetooth" Compatible Type) |
*d |
Portable Audio Player ("Bluetooth" Compatible Type) |
|
*e |
"Bluetooth" Wireless Connection |
- |
- |
(a) "Bluetooth" is a trademark owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
(b) "Bluetooth" is a wireless connection technology that uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
HINT:
The communication performance of "Bluetooth" may vary depending on obstructions or radio wave conditions between communication devices, electromagnetic radiation, communication device sensitivity or antenna capacity.
(c) Hands-free function
(1) The "Bluetooth" built-in navigation receiver assembly and a "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phone* can be connected using a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. This enables the use of the hands-free function on the cellular phone even if the phone is in a pocket or bag. For this reason, it is not necessary to use a connector or cable to connect the cellular phone.
- *: Some versions of "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phones may not function properly.
(2) The hands-free function uses a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. A "Bluetooth" wireless connection can be affected by uncertain elements, such as vehicle location, time of day, etc. Therefore, problems related to establishing connection may be caused temporarily by "Bluetooth" connection conditions. It is necessary to check the frequency of occurrence, connection conditions using another cellular phone, etc. when performing diagnosis.
(3) Compatible hands-free devices
|
Required "Bluetooth" specifications |
Ver. 1.1 |
|
Compatible profiles |
|
|
Maximum number of hands-free devices that can be registered (including audio devices) |
5 |
- *1: This profile is necessary when using the hands-free function.
- *2: This profile is necessary when using the message function.
HINT:
- "Bluetooth" compatible cellular phone can be checked at http:// www.toyota.com/entune/.
- The amount of remaining battery charge displayed on the navigation receiver assembly may be different from that of the "Bluetooth" device.
(d) "Bluetooth" audio function
(1) The "Bluetooth" built-in navigation receiver assembly and a "Bluetooth" compatible portable audio player* can be connected using a "Bluetooth" wireless connection. This enables files stored in the portable audio player to be heard from the vehicle speakers. In addition, operations such as play/stop can be performed directly from the navigation receiver assembly.
- *: Some versions of "Bluetooth" compatible audio players may not be able to operate the "Bluetooth" function, or music may play, but functions available using the navigation receiver assembly may be limited.
(2) Compatible "Bluetooth" audio devices
|
Required "Bluetooth" specifications |
Ver. 2.0 or higher (Ver. 3.0+EDR or higher recommended) |
|
Compatible profiles |
|
|
Maximum number of audio devices that can be registered |
5 |
HINT:
The amount of remaining battery charge displayed on the navigation receiver assembly may be different from that of the "Bluetooth" device.
7. RADIO DESCRIPTION
(a) Radio frequency band
(1) Radio broadcasts use the radio frequency bands shown in the table below.
.png)
(b) Service area
(1) The service areas of AM and FM broadcasts are vastly different. Sometimes an AM broadcast can be received very clearly but an FM stereo broadcast cannot. FM stereo has the smallest service area, and is prone to pick up static and other types of interference such as noise.
.png) Text in Illustration
Text in Illustration
|
*a |
FM (Stereo) |
|
*b |
FM (Monaural) |
|
*c |
AM |
(c) Radio reception problems
HINT:
In addition to static, other problems such as "phasing", "multipath" and "fade out" exist. These problems are not caused by electrical noise, but by the radio signal propagation method itself.
(1) Phasing
AM broadcasts are susceptible to electrical interference and another kind of interference called phasing. Occurring only at night, phasing is the interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off the ionosphere and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter.
.png) Text in Illustration
Text in Illustration
|
*a |
Phasing |
|
*b |
Ionosphere |
(2) Multipath
Multipath is a type of interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off buildings or mountains and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter.
.png) Text in Illustration
Text in Illustration
|
*a |
Multipath |
(3) Fade out
Fade out is caused by objects (buildings, mountains and other large obstructions) that deflect part of a signal, resulting in a weaker signal when the object is between the transmitter and vehicle. High frequency radio waves, such as FM broadcasts, are easily deflected by obstructions. Low frequency radio waves, such as AM broadcasts, are less likely to be deflected.
.png) Text in Illustration
Text in Illustration
|
*a |
Fade Out |
(d) Noise problem
Technicians must have a clear understanding about each customer's noise complaint. Use the following table to diagnose noise problems.
|
Radio Frequency |
Noise Occurrence Condition |
Presumable Cause |
|---|---|---|
|
AM |
Noise occurs in a specific area |
Foreign noise |
|
Noise occurs when listening to an intermittent broadcast |
An identical program transmitted from multiple towers can cause noise where the signals overlap |
|
|
Noise occurs only at night |
Signal phasing |
|
|
FM |
Noise occurs while driving in a specific area |
Multipath resulting from a change in FM frequency |
8. "HD Radio" FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ "HD Radio" Function)
(a) The "HD Radio" system is a radio system that broadcasts in the IBOC (In-Band On-Channel) form that the iBiquity Co. has developed. By expanding the bandwidth per channel of conventional FM/AM bands, digital audio and data signals are additionally transmitted.
"HD Radio" technology is manufactured under license from iBiquity Digital Corporation. U.S. and Foreign Patents. "HD Radio" and the HD and "HD Radio" logos are proprietary trademarks of iBiquity Digital Corporation.
Information for the music currently being listened to is stored in the system and can be transmitted to an "iPod" connected to the system. The information transferred to the "iPod" can be used for purchasing the music through the "iTunes" music store.
Also, traffic and weather information can be received and displayed on the navigation screen.
9. SDARS SYSTEM FUNCTION OUTLINE (w/ SDARS System)
(a) Satellite Digital Audio Radio Service (SDARS) is a satellite digital radio broadcast provided by Sirius XM Radio Inc. The broadcast (pay-type) is performed through satellites and terrestrial repeater networks. Several unique channels are available, and even if a vehicle changes locations, the same information can be received without breaks. Information such as song names, broadcast station names, etc. can be received.
NOTICE:
To receive audio-visual pay-type broadcasts, the customer must enter into a pay-type contract with XM Satellite Radio Inc. After entering into a contract, registration of the XM Radio ID is necessary. Also, if parts are replaced, the XM Radio ID must be re-registered.
HINT:
When disconnecting the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal, the broadcast station logo data will be initialized. It takes a while for the broadcast station logo data to be updated to the latest one.
10. VEHICLE CUSTOMIZATION OUTLINE
(a) Customization of functions can also be customized on the multi-display screen. Refer to Owner's Manual for further information on customizable items for the navigation system.
HINT:
- Items available for customization via the navigation system can also be customized by using the Techstream.
- Some customize parameters displayed on the Techstream will be displayed on the vehicle customization screen for the navigation system. Users can customize these items.
11. AUTOMATIC SOUND LEVELIZER (ASL) FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The Automatic Sound Levelizer (ASL) function automatically adjusts the audio system volume level in order to compensate for increased vehicle noise (vehicle noise tends to increase as vehicle speed increases). The ASL adjusts the volume level based upon vehicle speed signals sent from the combination meter assembly.
12. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(a) AVC-LAN Outline (for 13 Speakers)
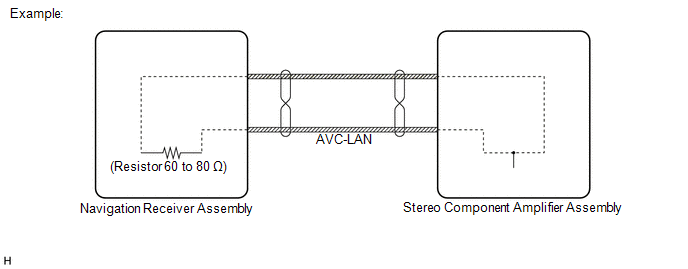
(1) Components of the navigation system communicate with each other via the AVC-LAN.
(2) The AVC-LAN uses a twisted pair of wires for its communication lines.
(3) The master unit of the AVC-LAN is the navigation receiver assembly.
HINT:
- The navigation receiver assembly has the resistance (60 to 80 Ω) necessary for communication.
- If a short or open occurs in the AVC-LAN circuit, communication is interrupted and the system will not operate normally.
(b) CAN Communication Outline
(1) The navigation system uses CAN communication between the navigation receiver assembly and ECUs.
(c) LVDS Communication Outline (w/ SDARS System)
(1) The navigation system uses LVDS communication, between the navigation receiver assembly and stereo component tuner assembly.
(2) If a short or open occurs in the LVDS communication line, communication is interrupted and the system will not operate normally.
13. DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION OUTLINE
(a) The navigation system has a diagnostic function.
 System Diagram
System Diagram
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
...
 How To Proceed With Troubleshooting
How To Proceed With Troubleshooting
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
HINT:
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot the navigation system.
*: Use the Techstream.
PROCEDURE
1.
VEHICLE BROUGHT TO ...
Other materials about Toyota Venza:
ECM Power Source Circuit
DESCRIPTION
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the battery voltage is applied to IGSW
of the ECM. The output signal from the MREL terminal of the ECM causes a current
to flow to the coil, closing the contact of the engine room junction block assemb ...
Combination Meter ECU Communication Stop Mode
DESCRIPTION
Detection Item
Symptom
Trouble Area
Combination Meter ECU Communication Stop Mode
"Combination Meter" is not displayed on "CAN Bus Check" screen
of t ...
Customize Parameters
CUSTOMIZE PARAMETERS
1. CUSTOMIZING FUNCTION WITH TECHSTREAM (REFERENCE)
HINT:
The following items can be customized.
NOTICE:
When the customer requests a change in a function, first make sure that
the function can be customized.
Record th ...
0.1414
